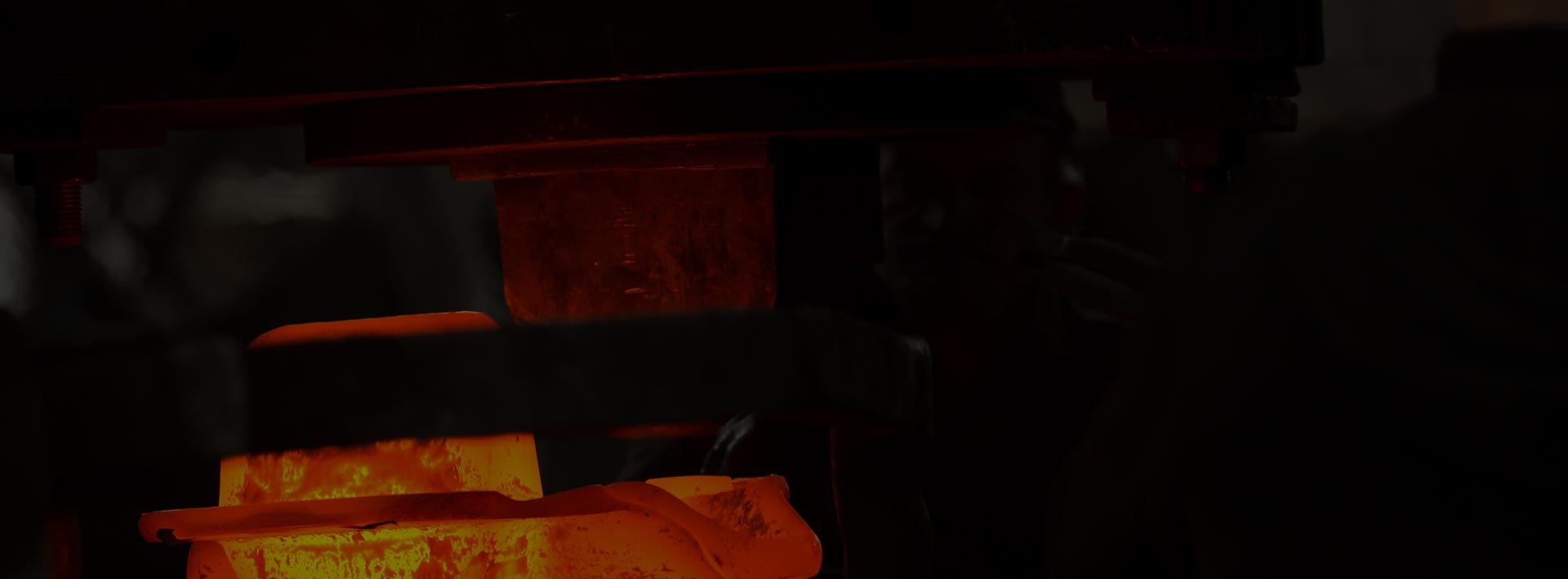
Forging
It is a hot forming of metal into a required geometry to achieve a desired strength in mechanical properties
- Customised Chemistry Composition
- Induction Hardening
- Deep Hole Drilling
- Semi-Finish / Finish Machining
- Alloy Steel (4130, 4140, 4145H, 4340, 8630, F22 etc)
- Carbon Steel (A105, A350, X52 – X80 etc)
- Stainless Steel (304, 316/316L, 317/317L, 410 etc)
- Special Steel (Duplex, Super Duplex, Nickel Alloy, etc)
- Customised Steel Grade to your requirements.

- Shape Forged
 Ring Rolling
Ring Rolling

Ring rolled forging is produced from bar stocked, upset, pierced and ring rolled to meet ID and OD requirements.
Ring rolling is using a ring of smaller diameter, rolling into a precise ring of larger diameter and a reduced cross section. This is accomplished by the use of two rollers, one driven and one idle, acting on either side of the ring’s cross section
Advantages of Ring Rolled Forging:
- The forming of the material will impart the ring with a grain orientation that gives it enhanced strength relative to most applications
Common Application:
- Casing Connectors;
- Gears;
- Spacers;

This forging process is forming a metal into the required shape by way of force hammering or hydraulic pressing
In open-die forging, a hydraulic press or hammer delivers a force to form the workpiece, which is manually or remotely operated, in which case toolings are employed, to shape the metal to the desired geometry
- Reduced chance of voids
- Better fatigue resistance
- Improved microstructure
- Continuous grain flow
- Finer grain size
- Greater strength
- Casing Heads
- Spools
- Flanges
A process where the pre-determined metal input is placed between two engraved die and formed to shape by hammering or compression
- Low recurring costs for each part
- Consistency of the part configuration
- Good for mass production
- Valve Bodies
- Shell
This forging process is forming a metal into the required shape by way of force hammering or hydraulic pressing without any additional tooling
- Reduces machining and material wastage
- Stabilizers
- Block Valves
- Heavy Wall Tubes
- Adaptors